Definition
A Frequency Response Function (FRF) is a function used to quantify the response of a system to an excitation, normalized by the magnitude of this excitation, in the frequency domain.
For instance, impacting a structure with an impact hammer and measuring its structural response with an accelerometer normalized by the injected force, a structural FRF is obtained between the two points. Then the information of the modal response of the structure is included in the FRF, in particular modal damping and natural frequencies.
Application of the vibration FRF to e-NVH
The structural response of electrical machines under electromagnetic excitations is generally quantified using the normal complex displacement [m] of the envelopped nodes (stator or rotor), while the excitation of the structure is quantified using equivalent magnetic forces per tooth [N]. The vibration FRF unit is thefore in [m/N].
The FRF can be expressed at each point of vibrating surfaces, or as a RMS value of the velocity over the vibrating surface(s) responsible for acoustic noise radiation. This average vibration velocity can be used as an indicator of the Sound Power Level radiated by the electrical machine assuming that the modal radiation efficiency is close to one (ERP model).
The response of the rotor and/or stator under magnetic forces can be quantified using different approaches: the stator teeth can be excited by radial & circumferential normalized tooth forces, giving as many FRF as the stator teeth number, or they can be excited by the Maxwell stress waves, giving as many FRF as the number of relevant wavenumbers coming from a Fourier decomposition along the airgap.
Application of the vibration FRF to Manatee
The second method is used in the Electromagnetic Vibration Synthesis algorithm of Manatee software.
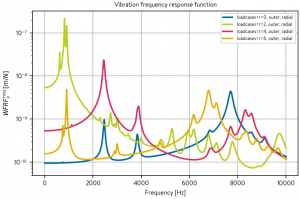
An example of vibration FRF is given in the following figure. One can see that the FRF is maximum when there is a resonance, for instance when the FRF of Maxwell stress wavenumber r=2 meets the natural frequencies of the elliptical model (2,0) of the stator stack.
Application of the acoustic FRF to e-NVH
The acoustic response of electrical machines under electromagnetic excitations is generally quantified using the Sound Power Level radiated by the outer yoke (stator or rotor), while the excitation of the structure is quantified using equivalent magnetic forces per tooth [N]. The acoustic FRF unit is thefore in [W/N^2] as the acoustic power evolves with the vibration to the power 2.
The acoustic FRF can also be locally expressed using Sound Pressure Level on a pre-defined acoustic mesh simulating virtual microphones around the outer yoke.